Inside this article we will see CakePHP 4 How to work with one to many relationship. Article contains classified information about relationship in cakephp. We will see an example of using one to many relation which makes you understand of cakephp association.
A one-to-many relationship is a type of cardinality that refers to the relationship between two entities A and B in which one element of A may only linked to one or multiple elements of B.
For example, we have two tables like employees and posts. Single employee can have one or multiple posts into posts table which will be one to many relationship.
Learn More –
- CakePHP 4 How To Work with MySQL Inner Join Tutorial
- CakePHP 4 How To Work with MySQL Left Join Tutorial
- CakePHP 4 How To Work with MySQL Right Join Tutorial
- CakePHP 4 How To Work With One To One Relationship
Let’s get started.
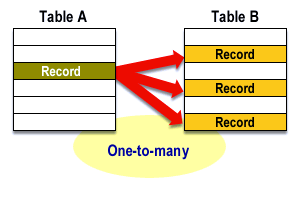
What is one-to-many relationship?
A one-to-many relationship is a type of cardinality that refers to the relationship between two entities A and B in which one element of A may only linked to one or multiple elements of B.
Here,
You can see we have two tables Table1 and Table2. A single row of Table1 can have one or multiple associated data in Table2. This is kind of one to many row between tables.
CakePHP 4 Installation
To create a CakePHP project, run this command into your shell or terminal. Make sure composer should be installed in your system.
$ composer create-project --prefer-dist cakephp/app:~4.0 mycakephp
Above command will creates a project with the name called mycakephp.
Create Database
To create a database, either we can create via Manual tool of PhpMyadmin or by means of a mysql command.
CREATE DATABASE mydatabase;Successfully, we have created a database.
Database Connection
Open app_local.php file from /config folder. Search for Datasources. Go to default array of it.
You can add your connection details here to connect with your database. It will be like this –
//...
'Datasources' => [
'default' => [
'host' => 'localhost',
/*
* CakePHP will use the default DB port based on the driver selected
* MySQL on MAMP uses port 8889, MAMP users will want to uncomment
* the following line and set the port accordingly
*/
//'port' => 'non_standard_port_number',
'username' => 'root',
'password' => 'sample@123',
'database' => 'mydatabase',
/*
* If not using the default 'public' schema with the PostgreSQL driver
* set it here.
*/
//'schema' => 'myapp',
/*
* You can use a DSN string to set the entire configuration
*/
'url' => env('DATABASE_URL', null),
],
//...
//...
You can pass host, username, password and database.
Successfully, you are now connected with the database.
Create Migrations
Open project into terminal and run bake console commands to create migrations for application.
$ bin/cake bake migration CreateEmployees
$ bin/cake bake migration CreatePostsAbove commands will create two migration files – 20220326133952_CreateEmployees.php and 20220326134000_CreatePosts.php.
Open 20220326133952_CreateEmployees.php and write this following code into it.
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
use Migrations\AbstractMigration;
class CreateEmployees extends AbstractMigration
{
public function change()
{
$table = $this->table('employees');
$table->addColumn("name", "string", [
"limit" => 50,
"null" => false
]);
$table->addColumn("email", "string", [
"limit" => 50,
"null" => false
]);
$table->addColumn("mobile", "string", [
"limit" => 20,
"null" => false
]);
$table->create();
}
}
It will create employees table in database.
Open 20220326134000_CreatePosts.php and write this following code into it.
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
use Migrations\AbstractMigration;
class CreatePosts extends AbstractMigration
{
public function change()
{
$table = $this->table('posts');
$table->addColumn("employee_id", "integer", [
"limit" => 5
]);
$table->addColumn("title", "string", [
"limit" => 50,
"null" => false
]);
$table->addColumn("description", "text", [
"null" => true
]);
$table->create();
}
}
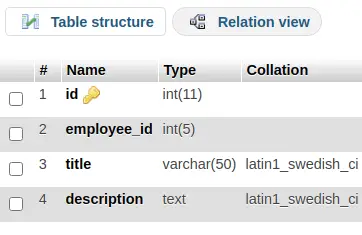
It will create posts table into database.
Run Migration
Back to terminal and run this command to create tables.
$ bin/cake migrations migrateTable: employees
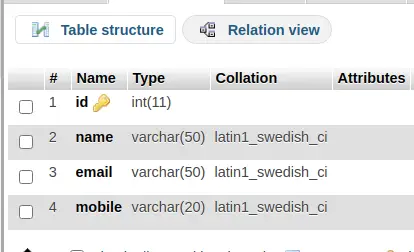
Table: posts
Sample Data For Tables
We will insert some fake data to test our application. Here, we have some mysql queries, you can copy and run for fake data.
Fake data for employees table.
-- -- Dumping data for table `employees` -- INSERT INTO `employees` (`id`, `name`, `email`, `mobile`) VALUES (1, 'Sanjay Kumar', 'sanjay@gmail.com', '1234567895'), (2, 'Ashish Kumar', 'ashish@gmail.com', '7412589635'), (3, 'Vijay Kumar', 'vijay@gmail.com', '9632587410');
Fake data for posts table.
-- -- Dumping data for table `posts` -- INSERT INTO `posts` (`id`, `employee_id`, `title`, `description`) VALUES (1, 1, 'Post 1', 'Sample Post Content 1'), (2, 1, 'Post 2', 'Sample Post Content 2'), (3, 2, 'Post 3', 'Sample Post Content 3'), (4, 3, 'Post 4', 'Sample Post Content 4');
Create Model & Entity
Now, we need to models and entities for application. Back to terminal and run these commands.
$ bin/cake bake model Employees --no-rules --no-validation
$ bin/cake bake model Posts --no-rules --no-validationIt will create EmployeesTable.php and Employee.php for Employees. Also PostsTable.php and Post.php in folders of /src/Model/Table and /src/Model/Entity.
Open EmployeesTable.php and write this following code into it.
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Model\Table;
use Cake\ORM\Table;
class EmployeesTable extends Table
{
public function initialize(array $config): void
{
parent::initialize($config);
$this->setTable('employees');
$this->setPrimaryKey('id');
$this->hasMany('emp_posts', [
'className' => 'Posts',
]);
}
}
Concept
$this->hasMany('emp_posts', [
'className' => 'Posts',
]);emp_posts is the association name between employees and posts tables. We will use this key to get data relational data between employees and posts table. Here, a single employee can have one or multiple posts into posts table.
Open PostsTable.php and write this following code into it.
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Model\Table;
use Cake\ORM\Table;
class PostsTable extends Table
{
public function initialize(array $config): void
{
parent::initialize($config);
$this->setTable('posts');
$this->setPrimaryKey('id');
}
}
Create Controller & Run Application
Back to terminal and run this bake console command to create controller.
$ bin/cake bake controller Site --no-actionsIt will create SiteController.php into /src/Controller folder. Open this file and write this code into it.
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
namespace App\Controller;
class SiteController extends AppController
{
public function initialize(): void
{
parent::initialize();
$this->loadModel("Employees");
$this->autoRender = false;
}
public function getDetails()
{
$employees = $this->Employees->find("all")->contain([
"emp_posts"
])->toList();
echo "<pre>";
print_r($employees);
}
}
Concept
Single employee is connected with one or more details of Posts table.
$employees = $this->Employees->find("all")->contain([
"emp_posts"
])->toList();Once we execute this code then we will get output like this. It will dump data into output screen.

Let’s iterate over arrays, and read row by row data from it.
//...
if (count($employees) > 0) {
foreach ($employees as $emp) {
$posts = $emp->emp_posts; // contains one or more posts
}
}
We hope this article helped you to learn CakePHP 4 How To Work With One To Many Relationship Tutorial in a very detailed way.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for PHP & it’s framework, WordPress, Node Js video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
Read more