Inside this article we will see the concept of Laravel 9 Seed Database Using Faker Library. Article contains classified information about database seeding concept.
If we have a large scale application in laravel and for testing we want huge amount of data then this concept is very useful to seed test data into table.
Faker is a PHP library that generates fake data for you. In Laravel we have faker available by default. We can use it’s all methods and properties to generate data.
In Laravel there are several ways by which we can seed fake data to database for testing purpose. Here, we will see how to seed fake data into database table using faker and factory concept.
Learn More –
- Laravel 9 Has One Through Eloquent Relationship Tutorial
- Laravel 9 How To Seed Database Using Seeder File Tutorial
- Laravel 9 How To Send Email To Multiple Users Tutorial
- Laravel 9 Many to Many Eloquent Relationship Tutorial
Let’s get started.
Laravel Installation
Open terminal and run this command to create a laravel project.
composer create-project laravel/laravel myblogIt will create a project folder with name myblog inside your local system.
To start the development server of laravel –
php artisan serveURL: http://127.0.0.1:8000
Assuming laravel already installed inside your system.
Create Database & Connect
To create a database, either we can create via Manual tool of PhpMyadmin or by means of a mysql command.
CREATE DATABASE laravel_app;
To connect database with application, Open .env file from application root. Search for DB_ and update your details.
DB_CONNECTION=mysql DB_HOST=127.0.0.1 DB_PORT=3306 DB_DATABASE=laravel_app DB_USERNAME=root DB_PASSWORD=root
Create Migration
We will create a students table using migration and then we seed test data inside it.
Open project into terminal and run this command to create migration file.
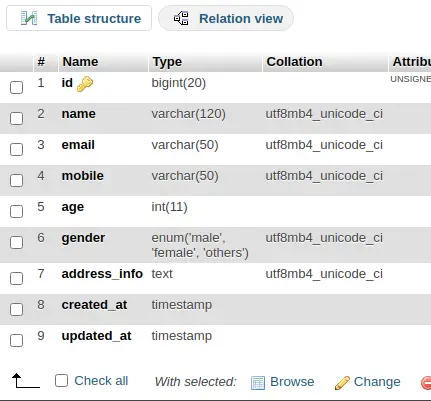
$ php artisan make:migration create_students_tableIt will create 2022_04_17_031027_create_students_table.php file inside /database/migrations folder. Open migration file and write this following code into it.
The code is all about for the schema of students table.
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('students', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string("name", 120);
$table->string("email", 50)->nullable();
$table->string("mobile", 50)->nullable();
$table->integer("age");
$table->enum("gender", ["male", "female", "others"]);
$table->text("address_info");
$table->timestamp("created_at")->useCurrent();
$table->timestamp("updated_at")->useCurrent();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('students');
}
};
Run Migration
Back to terminal and run this command.
$ php artisan migrateIt will create students table inside database.
Create Model
Back to project terminal and run this command to create model.
$ php artisan make:model StudentIt will create Student.php file inside /app/Models folder. This file will help when we generate data using factory and insert into table.
Create Data Factory
Next,
Copy this command and run into terminal to create a factory file.
$ php artisan make:factory StudentFactoryIt will create a file StudentFactory.php inside /database/factories folder. Open file and write this following code into it.
<?php
namespace Database\Factories;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\Factory;
/**
* @extends \Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\Factory<\App\Models\Student>
*/
class StudentFactory extends Factory
{
/**
* Define the model's default state.
*
* @return array<string, mixed>
*/
public function definition()
{
return [
"name" => $this->faker->name(),
"email" => $this->faker->safeEmail,
"mobile" => $this->faker->phoneNumber,
"age" => $this->faker->numberBetween(25, 45),
"gender" => $this->faker->randomElement([
"male",
"female",
"others"
]),
"address_info" => $this->faker->address
];
}
}
Call Model Factory
Open DatabaseSeeder.php from /database/seeders folder. Load model and factory.
<?php
namespace Database\Seeders;
use Illuminate\Database\Console\Seeds\WithoutModelEvents;
use Illuminate\Database\Seeder;
class DatabaseSeeder extends Seeder
{
/**
* Seed the application's database.
*
* @return void
*/
public function run()
{
\App\Models\Student::factory(100)->create();
}
}
Concept
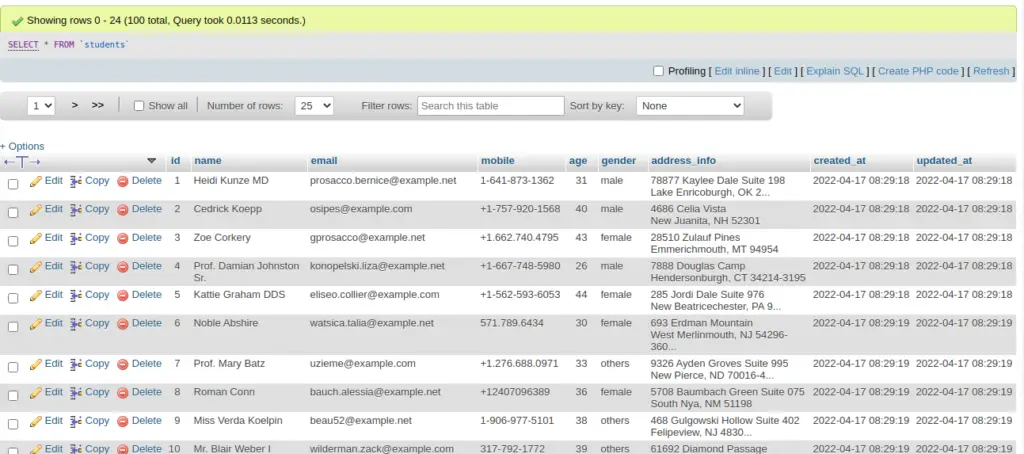
\App\Models\Student::factory(100)->create();It will generate 100 fake rows of student using StudentFactory.php file and save into students table.
Run Data Seeder
Back to project terminal and run this command to run factory to seed fake data.
$ php artisan db:seedIt will generate and save fake data into students table.
We hope this article helped you to learn about Laravel 9 Seed Database Using Faker Library Tutorial in a very detailed way.
[do_widget “buy me a coffee”]
Online Web Tutor invites you to try Skillshare free for 1 month! Learn CakePHP 4, Laravel APIs Development, CodeIgniter 4, Node Js, etc into a depth level. Master the Coding Skills to Become an Expert in Web Development. So, Search your favourite course and enroll now. Click here to join.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for PHP & it’s framework, WordPress, Node Js video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.