In Laravel 10, creating unique slugs is a common necessity when developing apps that use friendly URLs, SEO optimisation, or unique resource identifiers. A slug is a URL-friendly string representation that is commonly used to generate human-readable and search engine-friendly URLs.
In this detailed tutorial, we will walk you through the process of creating unique slugs in Laravel 10. We will look at various strategies and best practises for ensuring that generated slugs are unique across your application, preventing conflicts and preserving data integrity.
Read More: How To Get HTTP Hostname In Laravel 10 Tutorial
Slugs are frequently used in search engine optimisation (SEO) to increase the ranking of a website in search results by making URLs more user-friendly.
For example, in the URL https://www.example.com/blog/how-to-write-a-blog-post, “how-to-write-a-blog-post” is the slug.
Let’s get started.
Laravel Installation
Open terminal and run this command to create a laravel project.
composer create-project laravel/laravel myblogIt will create a project folder with name myblog inside your local system.
To start the development server of laravel –
php artisan serveURL: http://127.0.0.1:8000
Assuming laravel already installed inside your system.
Create Database & Connect
To create a database, either we can create via Manual tool of PhpMyadmin or by means of a mysql command.
CREATE DATABASE laravel_app;
To connect database with application, Open .env file from application root. Search for DB_ and update your details.
DB_CONNECTION=mysql DB_HOST=127.0.0.1 DB_PORT=3306 DB_DATABASE=laravel_app DB_USERNAME=root DB_PASSWORD=root
Read More: How to Check If a File Exists in Laravel 10 Tutorial
Create Model & Migration
Open project into terminal and run this command to create model and migration file.
Model file is one which helps application to communicate with database table and migration file creates schema of table.
$ php artisan make:model Product -mThis command create two different files – a Model file and a Migration file. -m is for migration file.
- Proudct.php model file inside /app/Models folder.
- 2023_03_15_030914_create_products_table.php Migration file inside /database/migrations.
Open {timestamp}_create_products_table.php migration file and write this update code.
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('products', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string("name", 70);
$table->string("slug", 100)->nullable();
$table->text("description")->nullable();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('products');
}
};
Run Migration
Back to terminal and run this artisan migrate command to run migrations.
$ php artisan migrateTable: products
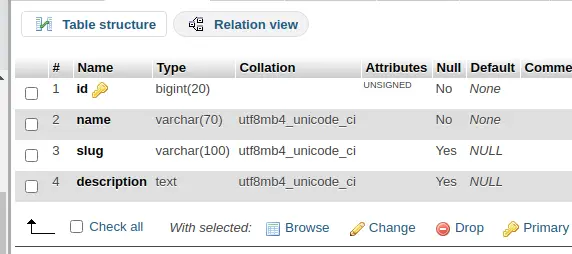
Open Product.php from /app/Models folder and write this following code into it.
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
use Illuminate\Support\Str;
class Product extends Model
{
use HasFactory;
protected $fillable = [
'name', 'slug', 'description'
];
public $timestamps = false;
/**
* Boot the model.
*/
protected static function boot()
{
parent::boot();
static::created(function ($product) {
$product->slug = $product->createSlug($product->name);
$product->save();
});
}
/**
* Write code on Method
*
* @return response()
*/
private function createSlug($name)
{
if (static::whereSlug($slug = Str::slug($name))->exists()) {
$max = static::whereName($name)->latest('id')->skip(1)->value('slug');
if (isset($max[-1]) && is_numeric($max[-1])) {
return preg_replace_callback('/(\d+)$/', function ($mathces) {
return $mathces[1] + 1;
}, $max);
}
return "{$slug}-2";
}
return $slug;
}
}
whereSlug is dynamic method created from the name of column. where{ColumnName}. whereName() is for name column.
Here,
We are checking that slug should be unique of every inserted product.
Examples for some slug
laravel-10-product-upload
laravel-10-product-upload-2
laravel-10-product-upload-3
laravel-10-product-upload-4Read More: Laravel 10 How To Change Name And From Address in Email
Create Application Controller
Back to terminal and run this artisan command
$ php artisan make:controller ProductControllerIt will create a file ProductController.php inside /app/Http/Controllers folder.
Open this controller file and write this code into it.
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Models\Product;
class ProductController extends Controller
{
public function addProduct()
{
$product = Product::create([
"name" => "Laravel 10 Sample Product",
"description" => "Sample data"
]);
dd($product);
}
}
- Create & Save product into database table “products”.
- Automatically the boot method what we have created in Product model will be used. We have used the concept of model event static::created
- Product::create(), we have passed name and description value and also slug value automatically comes from model and will insert into table.
Add Route
Open web.php from /routes folder. Add this route into it.
//...
use App\Http\Controllers\ProductController;
Route::get('product', [ProductController::class, 'addProduct']);
//...
Application Testing
Run this command into project terminal to start development server,
php artisan serveURL – http://127.0.0.1:8000/product
When you hit this url multiple times, it will insert new product rows inside products table. One thing we can notice is here about generated slug value, It is unique for all rows.
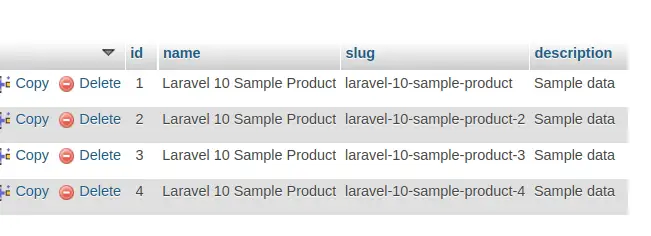
We hope this article helped you to learn about How To Generate Unique Slug in Laravel 10 Tutorial in a very detailed way.
Read More: Laravel 10 How To Add Image Into PDF Using DomPDF Library
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for PHP & it’s framework, WordPress, Node Js video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
Read more