Using the power of database relationships is critical in Laravel 10 for building powerful and efficient apps. The INNER JOIN is a key concept in relational databases that allows you to integrate data from several tables based on matching values in defined fields. INNER JOINS are essential for retrieving related data and generating useful insights from your database.
This tutorial will walk you through a detailed example of using INNER JOIN in Laravel 10 with MySQL. We’ll look at how to construct database relationships, create migration files, and run INNER JOIN queries to retrieve data from related tables.
Read More: Tyrone’s Unblocked Games – Play Online Games
Let’s get started.
Types of Joins
As per the documentation we have following types of joins available –
- Inner Join
- Left Join
- Right Join
- Cross Join
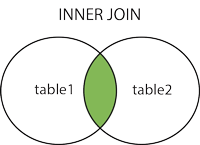
What is Inner Join?
Inner Join – This join brings the data on the basis of a common value condition between two or more than two tables. According to matched condition it will bring all data what we expected for. It remove those rows from result set which has no matched condition.
Laravel Installation
Open terminal and run this command to create a laravel project.
composer create-project laravel/laravel myblogIt will create a project folder with name myblog inside your local system.
To start the development server of laravel –
php artisan serveURL: http://127.0.0.1:8000
Assuming laravel already installed inside your system.
Create Database & Connect
To create a database, either we can create via Manual tool of PhpMyadmin or by means of a mysql command.
CREATE DATABASE laravel_app;
To connect database with application, Open .env file from application root. Search for DB_ and update your details.
DB_CONNECTION=mysql DB_HOST=127.0.0.1 DB_PORT=3306 DB_DATABASE=laravel_app DB_USERNAME=root DB_PASSWORD=root
Next,
Setup Migrations & Model
Create migrations and models for Employees and Projects table.
Read More: LiveLeak Alternatives
Open project into terminal and run this artisan command.
$ php artisan make:model Employee -mIt will create two files –
- Model file Employee.php inside /app/Models folder.
- Migration file 2023_08_11_062204_create_employees_table.php inside /database/migrations folder.
$ php artisan make:migration create_projects_tableIt will create a migration file 2023_08_11_062234_create_projects_table.php inside /database/migrations folder.
Open xxx_create_employees_table.php and write this following code into it.
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*/
public function up(): void
{
Schema::create('employees', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string("name", 50);
$table->string("email", 50);
$table->string("phone_no", 20);
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*/
public function down(): void
{
Schema::dropIfExists('employees');
}
};
Open xxx_create_projects_table.php and write this following code into it.
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*/
public function up(): void
{
Schema::create('projects', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->integer('employee_id')->unsigned();
$table->string("project_name", 100);
$table->foreign('employee_id')
->references('id')->on('employees')
->onDelete('cascade');
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*/
public function down(): void
{
Schema::dropIfExists('projects');
}
};
Migrate Migrations
Back to terminal and run this command to migrate all migrations.
$ php artisan migrateThis command will migrate all.
Insert Test Data (Tables)
We have some mysql queries which will insert test data to employees and projects table.
Read More: Laravel 10 How To Setup Ajax Request Tutorial
Copy command and run into SQL tab of mysql database.
-- -- Dumping data for table `employees` -- INSERT INTO `employees` (`id`, `name`, `email`, `phone_no`) VALUES (1, 'Sanjay Kumar', 'sanjay@gmail.com', '8527419630'), (2, 'Vijay Kumar', 'vijay@gmail.com', '9632587410'), (3, 'Ashish Kumar', 'ashish@gmail.com', '7896541356');
-- -- Dumping data for table `projects` -- INSERT INTO `projects` (`id`, `employee_id`, `project_name`) VALUES (1, 1, 'Project 4'), (2, 2, 'Project 7'), (3, 3, 'Project 50');
Create Controller
Open project into terminal and run this command.
$ php artisan make:controller SiteControllerIt will create SiteController.php file inside /app/Http/Controllers folder.
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Models\Employee;
class SiteController extends Controller
{
public function getData()
{
$data = Employee::join("projects", function ($join) {
$join->on("projects.employee_id", "=", "employees.id");
})->get();
echo "<pre>";
print_r($data);
}
}
There are 2 methods available by which you can use inner join concept.
Method #1
$data = Employee::join("projects", function ($join) {
$join->on("projects.employee_id", "=", "employees.id");
})->get();Method #2
$data = Employee::join("projects", "projects.employee_id", "=", "employees.id")->get();Read More: Namelix: The AI-Powered Business Name Generator Tool
Query will be,
select * from `employees` inner join `projects` on `projects`.`employee_id` = `employees`.`id`Add Route
Open web.php file from /routes folder.
//...
use App\Http\Controllers\SiteController;
Route::get("inner-join", [SiteController::class, "getData"]);
//...
Application Testing
Run this command into project terminal to start development server,
php artisan serveURL: http://127.0.0.1:8000/inner-join
You will get your data set at output screen.
Advanced Cases in Inner Join
Assuming these cases, you can take a hint from these.
Example 1: Laravel Eloquent Join() with 2 Tables
$users = User::join('posts', 'users.id', '=', 'posts.user_id') ->get(['users.*', 'posts.descrption']);Generated Query,
select `users`.*, `posts`.`descrption` from `users` inner join `posts` on `users`.`id` = `posts`.`user_id`Example 2: Laravel Eloquent Join() with 3 Tables
$users = User::join('posts', 'posts.user_id', '=', 'users.id') ->join('comments', 'comments.post_id', '=', 'posts.id') ->get(['users.*', 'posts.descrption']);Generated Query,
select `users`.*, `posts`.`descrption` from `users` inner join `posts` on `posts`.`user_id` = `users`.`id` inner join `comments` on `comments`.`post_id` = `posts`.`id`Example 3: Laravel Eloquent Join() with Multiple Conditions
$users = User::join('posts', 'posts.user_id', '=', 'users.id') ->where('users.status', 'active')
->where('posts.status','active')
->get(['users.*', 'posts.descrption']);Generated Query,
select `users`.*, `posts`.`descrption` from `users` inner join `posts` on `posts`.`user_id` = `users`.`id` where `users`.`status` = active and `posts`.`status` = activeWe hope this article helped you to learn about Laravel 10 MySQL Inner Join Example Tutorial in a very detailed way.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for PHP & it’s framework, WordPress, Node Js video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
Read more