Inside this article we will learn one more important concept of laravel i.e Laravel 9 REST API Development Using JWT Authentication. This will be step by step guide to create restful services from scratch.
REpresentational State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style that defines a set of constraints to be used for creating web services. REST API is a way of accessing web services in a simple and flexible way without having any processing.
In this article we will create a secure set of rest apis using laravel using JWT auth. We will use a JWT package to implement the concept of JWT authentication.
What we will do in this article –
- User Register API
- Login API
- Refresh Token API
- Logout API
- Create Todo API
- List Todo API
- Single Todo details API
- Update Todo API
- Delete Todo API
Above are the apis, we will create using jwt authentication.
Learn More –
- Laravel 9 REST API Development Using Passport Tutorial
- Laravel 9 REST API Development Using Sanctum Tutorial
- Laravel 9 Scout How To Add Full Text Search in Table
- Laravel 9 Seed Database Using Faker Library Tutorial
Let’s get started.
Laravel Installation
Open terminal and run this command to create a laravel project.
composer create-project laravel/laravel myblogIt will create a project folder with name myblog inside your local system.
To start the development server of laravel –
php artisan serveURL: http://127.0.0.1:8000
Assuming laravel already installed inside your system.
Create Database & Connect
To create a database, either we can create via Manual tool of PhpMyadmin or by means of a mysql command.
CREATE DATABASE laravel_app;
To connect database with application, Open .env file from application root. Search for DB_ and update your details.
DB_CONNECTION=mysql DB_HOST=127.0.0.1 DB_PORT=3306 DB_DATABASE=laravel_app DB_USERNAME=root DB_PASSWORD=root
Install And Configure Laravel JWT Auth
JSON Web Token (JWT) is an open standard (RFC 7519), and it represents a compact and self-contained method for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object.
Open project into terminal and run this command.
$ composer require php-open-source-saver/jwt-auth
Publish Provider
Back to project terminal and run this command.
$ php artisan vendor:publish --provider="PHPOpenSourceSaver\JWTAuth\Providers\LaravelServiceProvider"Generate JWT Secret Keys
$ php artisan jwt:secretIt will generate few JWT secret keys and save into .env file. You should see these keys into .env file. These keys handle the token encryption.
JWT_SECRET=ncXDYGJAU30WPY09AgijRXRnFppA3MhZGCG3sDnYhxOCRuFbaXbkYUzvfxg1BmPF
JWT_ALGO=HS256Configure AuthGuard
We need to make a few changes to configure Laravel to use the JWT AuthGuard to power the application authentication.
To configure guard, Open auth.php file from /config folder.
//...
'defaults' => [
'guard' => 'api',
'passwords' => 'users',
],
'guards' => [
'web' => [
'driver' => 'session',
'provider' => 'users',
],
'api' => [
'driver' => 'jwt',
'provider' => 'users',
],
],
//...Update User Model
When we install laravel setup, by default we get a model User.php inside /app/Models folder.
use PHPOpenSourceSaver\JWTAuth\Contracts\JWTSubject; // Add this
class User extends Authenticatable implements JWTSubject {}Open User.php and update with this code.
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\MustVerifyEmail;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User as Authenticatable;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable;
use PHPOpenSourceSaver\JWTAuth\Contracts\JWTSubject;
class User extends Authenticatable implements JWTSubject
{
use HasFactory, Notifiable;
/**
* The attributes that are mass assignable.
*
* @var array<int, string>
*/
protected $fillable = [
'name',
'email',
'password',
];
/**
* The attributes that should be hidden for serialization.
*
* @var array<int, string>
*/
protected $hidden = [
'password',
'remember_token',
];
/**
* The attributes that should be cast.
*
* @var array<string, string>
*/
protected $casts = [
'email_verified_at' => 'datetime',
];
/**
* Get the identifier that will be stored in the subject claim of the JWT.
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function getJWTIdentifier()
{
return $this->getKey();
}
/**
* Return a key value array, containing any custom claims to be added to the JWT.
*
* @return array
*/
public function getJWTCustomClaims()
{
return [];
}
}
Create Model & Migration For Todo
Open project into terminal and run this artisan command.
$ php artisan make:model Todo -m-m to create migration file as well.
Above command will generate two files. One is Model and second is migration file.
Model – Todo.php inside /app/Models folder
Migration – 2022_03_20_040948_create_todos_table.php inside /database/migrations
Open Todo.php and write this code into it.
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Todo extends Model
{
use HasFactory;
protected $fillable = [
'title',
'description'
];
}
Open Migration file 2022_03_20_040948_create_todos_table.php and write this code.
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('todos', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('title');
$table->string('description');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('todos');
}
};
Run Migration
Back to terminal and run this command to migrate.
$ php artisan migrateCreate Controllers
Back to terminal and run these artisan commands to create.
Auth Api Controller
$ php artisan make:controller AuthControllerThis command will create a file AuthController.php inside /app/Http/Controllers folder.
Todo Api Controller
$ php artisan make:controller TodoControllerThis command will create a file TodoController.php inside /app/Http/Controllers folder.
Now, we will start writing code inside all these controllers.
Open AuthController.php file and write this code into it.
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Auth;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Hash;
use App\Models\User;
class AuthController extends Controller
{
public function __construct()
{
$this->middleware('auth:api', ['except' => ['login', 'register']]);
}
public function login(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'email' => 'required|string|email',
'password' => 'required|string',
]);
$credentials = $request->only('email', 'password');
$token = Auth::attempt($credentials);
if (!$token) {
return response()->json([
'status' => 'error',
'message' => 'Unauthorized',
], 401);
}
$user = Auth::user();
return response()->json([
'status' => 'success',
'user' => $user,
'authorisation' => [
'token' => $token,
'type' => 'bearer',
]
]);
}
public function register(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'name' => 'required|string|max:255',
'email' => 'required|string|email|max:255|unique:users',
'password' => 'required|string|min:6',
]);
$user = User::create([
'name' => $request->name,
'email' => $request->email,
'password' => Hash::make($request->password),
]);
$token = Auth::login($user);
return response()->json([
'status' => 'success',
'message' => 'User created successfully',
'user' => $user,
'authorisation' => [
'token' => $token,
'type' => 'bearer',
]
]);
}
public function logout()
{
Auth::logout();
return response()->json([
'status' => 'success',
'message' => 'Successfully logged out',
]);
}
public function refresh()
{
return response()->json([
'status' => 'success',
'user' => Auth::user(),
'authorisation' => [
'token' => Auth::refresh(),
'type' => 'bearer',
]
]);
}
}
Open TodoController.php file and write this code into it.
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Models\Todo;
class TodoController extends Controller
{
public function __construct()
{
$this->middleware('auth:api');
}
public function index()
{
$todos = Todo::all();
return response()->json([
'status' => 'success',
'todos' => $todos,
]);
}
public function store(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'title' => 'required|string|max:255',
'description' => 'required|string|max:255',
]);
$todo = Todo::create([
'title' => $request->title,
'description' => $request->description,
]);
return response()->json([
'status' => 'success',
'message' => 'Todo created successfully',
'todo' => $todo,
]);
}
public function show($id)
{
$todo = Todo::find($id);
return response()->json([
'status' => 'success',
'todo' => $todo,
]);
}
public function update(Request $request, $id)
{
$request->validate([
'title' => 'required|string|max:255',
'description' => 'required|string|max:255',
]);
$todo = Todo::find($id);
$todo->title = $request->title;
$todo->description = $request->description;
$todo->save();
return response()->json([
'status' => 'success',
'message' => 'Todo updated successfully',
'todo' => $todo,
]);
}
public function destroy($id)
{
$todo = Todo::find($id);
$todo->delete();
return response()->json([
'status' => 'success',
'message' => 'Todo deleted successfully',
'todo' => $todo,
]);
}
}
Add API Routes
Open api.php from /routes folder. Add these routes into it.
//...
use App\Http\Controllers\AuthController;
use App\Http\Controllers\TodoController;
//...
Route::controller(AuthController::class)->group(function () {
Route::post('login', 'login');
Route::post('register', 'register');
Route::post('logout', 'logout');
Route::post('refresh', 'refresh');
});
Route::controller(TodoController::class)->group(function () {
Route::get('todos', 'index');
Route::post('todo', 'store');
Route::get('todo/{id}', 'show');
Route::put('todo/{id}', 'update');
Route::delete('todo/{id}', 'destroy');
});
Open terminal and run this artisan command to see all available routes.
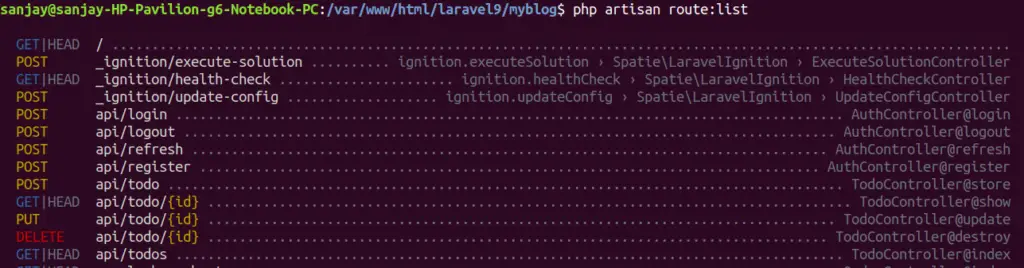
Application Testing
Run this command into project terminal to start development server,
php artisan serveRegister API
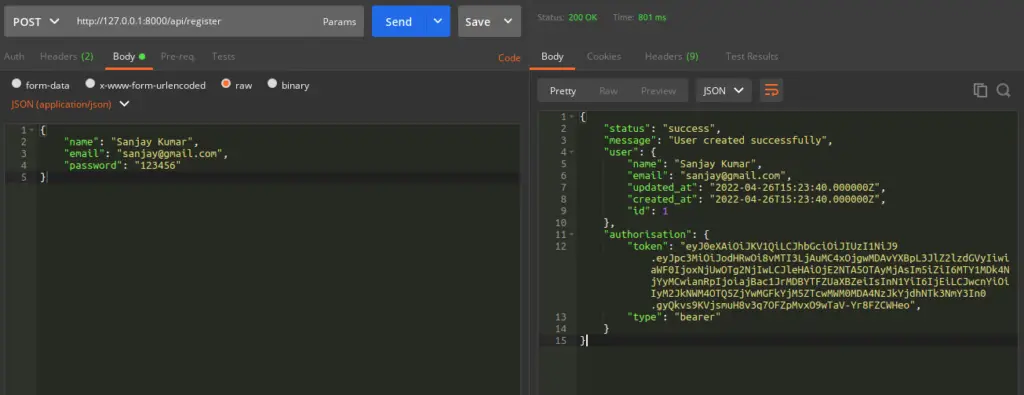
URL – http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/register
Method – POST
Header –
Content-Type:application/json
Accept:application/jsonBody –
{
"name": "Sanjay Kumar",
"email": "sanjay@gmail.com",
"password": "123456"
}
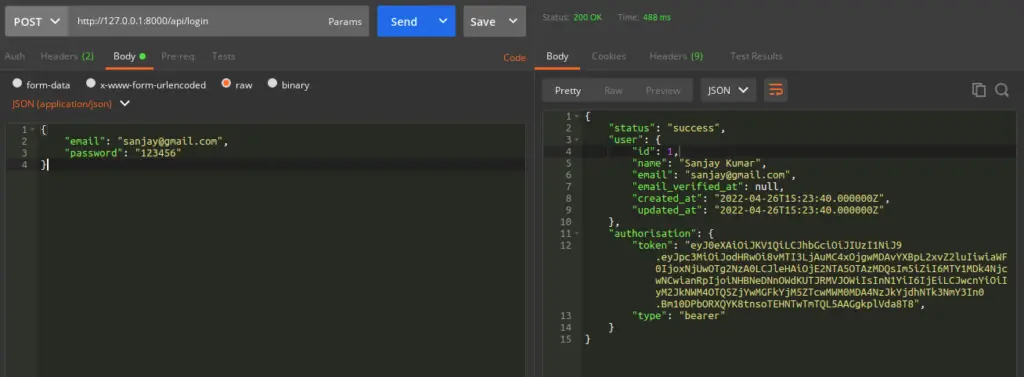
Login API
URL – http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/login
Method – POST
Header –
Content-Type:application/json
Accept:application/jsonBody –
{
"email": "sanjay@gmail.com",
"password": "123456"
}
Refresh Token API
URL – http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/refresh
Method – POST
Header –
Authorization:Bearer <token>
Accept:application/json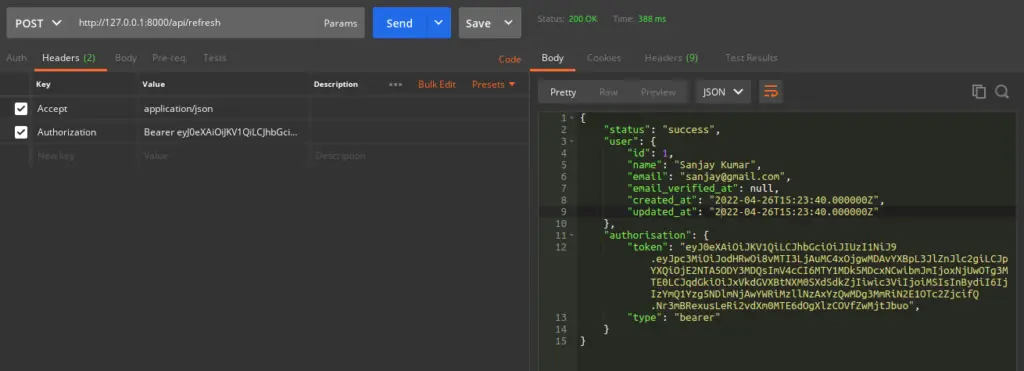
Logout API
URL – http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/logout
Method – POST
Header –
Authorization:Bearer <token>
Accept:application/json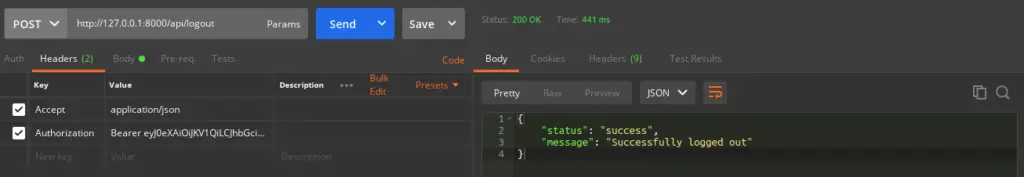
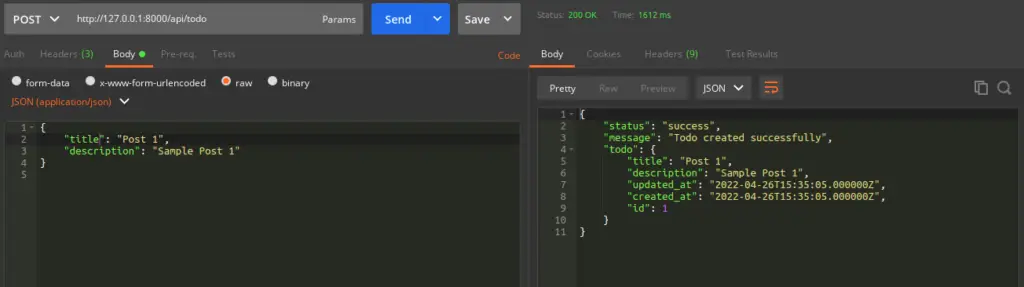
Create Todo API
URL – http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/todo
Method – POST
Header –
Content-Type:application/json
Authorization:Bearer <token>
Accept:application/jsonBody –
{
"title": "Post 1",
"description": "Sample Post 1"
}
List Todo API
URL – http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/todos
Method – GET
Header –
Authorization:Bearer <token>
Accept:application/json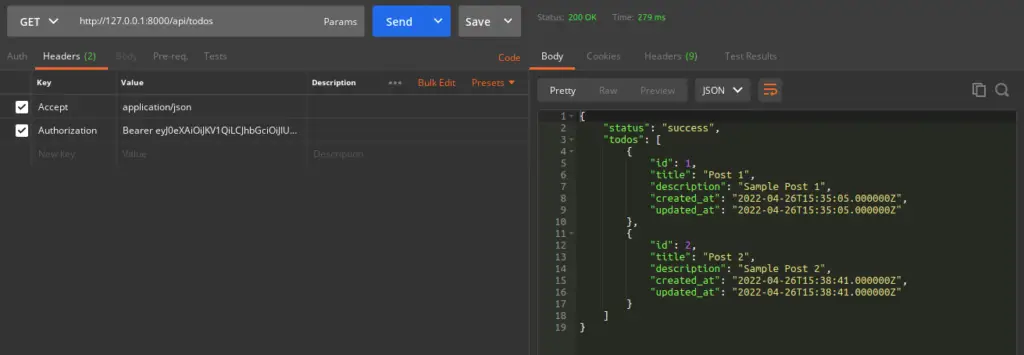
Single Todo Detail API
URL – http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/todo/1
Method – GET
Header –
Authorization:Bearer <token>
Accept:application/json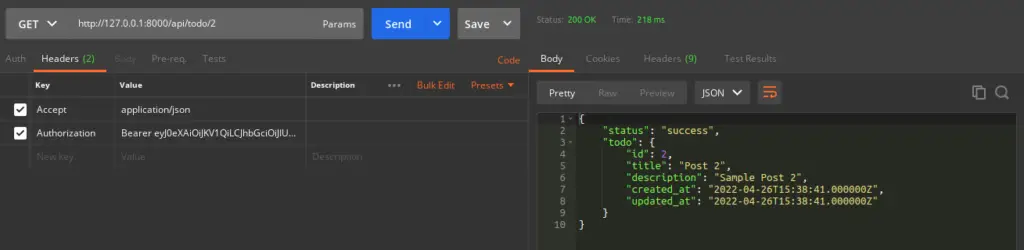
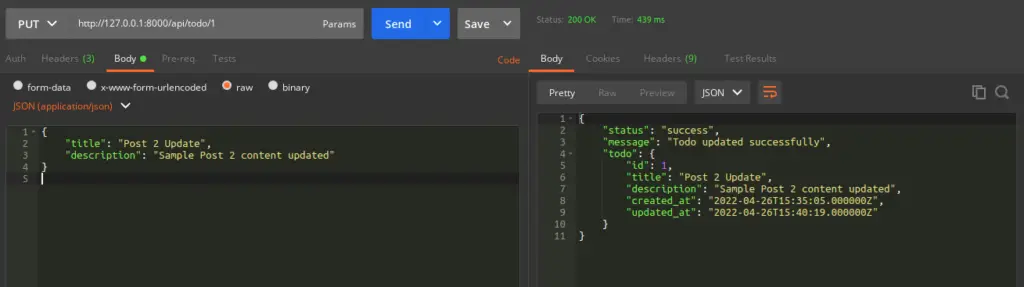
Update Todo API
URL – http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/todo/1
Method – PUT
Header –
Content-Type:application/json
Authorization:Bearer <token>
Accept:application/jsonBody –
{
"title": "Post 2 update",
"description": "Sample Post 2 content updated"
}
Delete Todo API
URL – http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/todo/1
Method – DELETE
Header –
Authorization:Bearer <token>
Accept:application/json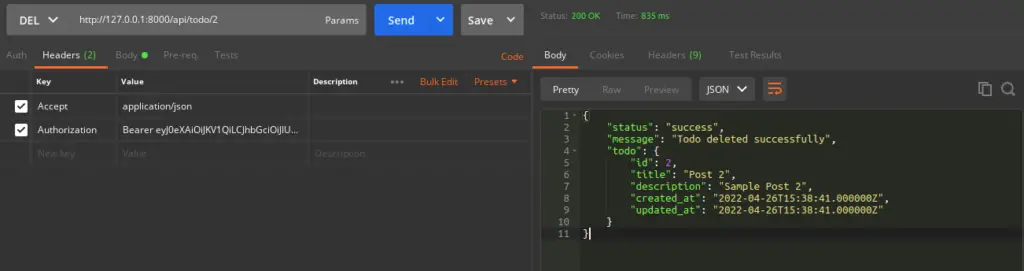
We hope this article helped you to learn about Laravel 9 REST API Development Using JWT Authentication in a very detailed way.
Online Web Tutor invites you to try Skillshike! Learn CakePHP, Laravel, CodeIgniter, Node Js, MySQL, Authentication, RESTful Web Services, etc into a depth level. Master the Coding Skills to Become an Expert in PHP Web Development. So, Search your favourite course and enroll now.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for PHP & it’s framework, WordPress, Node Js video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
