Inside this article we will see the concept of Laravel 9 yajrabox server side datatable tutorial. Yajrabox is nothing, it’s package by the help of which we will integrate server side datatable.
We will implement Ajax DataTable in Laravel i.e Yajrabox DataTable. Datatables provides searching, pagination, ordering, sorting and etc. You need to follow the given steps to implement server side datatable Yajrabox in Laravel.
Learn More –
- Laravel 9 Seed Database Using Faker Library Tutorial
- Laravel 9 Send Mail Using Gmail SMTP Server Tutorial
- Laravel 9 Stub Customization Step By Step Tutorial
Let’s get started.
Laravel Installation
Open terminal and run this command to create a laravel project.
composer create-project laravel/laravel myblogIt will create a project folder with name myblog inside your local system.
To start the development server of laravel –
php artisan serveURL: http://127.0.0.1:8000
Assuming laravel already installed inside your system.
Create Database & Connect
To create a database, either we can create via Manual tool of PhpMyadmin or by means of a mysql command.
CREATE DATABASE laravel_app;
To connect database with application, Open .env file from application root. Search for DB_ and update your details.
DB_CONNECTION=mysql DB_HOST=127.0.0.1 DB_PORT=3306 DB_DATABASE=laravel_app DB_USERNAME=root DB_PASSWORD=root
Create Migration
We will create a students table using migration and then we seed test data inside it.
Open project into terminal and run this command to create migration file.
$ php artisan make:migration create_students_tableIt will create 2022_04_17_031027_create_students_table.php file inside /database/migrations folder. Open migration file and write this following code into it.
The code is all about for the schema of students table.
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up()
{
Schema::create('students', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string("name", 120);
$table->string("email", 50)->nullable();
$table->string("mobile", 50)->nullable();
$table->integer("age");
$table->enum("gender", ["male", "female", "others"]);
$table->text("address_info");
$table->timestamp("created_at")->useCurrent();
$table->timestamp("updated_at")->useCurrent();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('students');
}
};
Run Migration
Back to terminal and run this command.
$ php artisan migrateIt will create students table inside database.
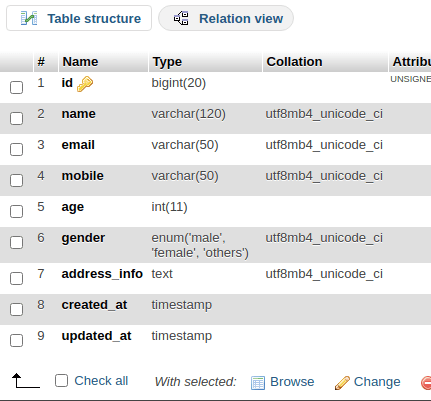
Create Model
Back to project terminal and run this command to create model.
$ php artisan make:model StudentIt will create Student.php file inside /app/Models folder. This file will help when we generate data using factory and insert into table.
Create Data Factory
Next,
Copy this command and run into terminal to create a factory file.
$ php artisan make:factory StudentFactoryIt will create a file StudentFactory.php inside /database/factories folder. Open file and write this following code into it.
<?php
namespace Database\Factories;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\Factory;
/**
* @extends \Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\Factory<\App\Models\Student>
*/
class StudentFactory extends Factory
{
/**
* Define the model's default state.
*
* @return array<string, mixed>
*/
public function definition()
{
return [
"name" => $this->faker->name(),
"email" => $this->faker->safeEmail,
"mobile" => $this->faker->phoneNumber,
"age" => $this->faker->numberBetween(25, 45),
"gender" => $this->faker->randomElement([
"male",
"female",
"others"
]),
"address_info" => $this->faker->address
];
}
}
Call Model Factory
Open DatabaseSeeder.php from /database/seeders folder. Load model and factory.
<?php
namespace Database\Seeders;
use Illuminate\Database\Console\Seeds\WithoutModelEvents;
use Illuminate\Database\Seeder;
class DatabaseSeeder extends Seeder
{
/**
* Seed the application's database.
*
* @return void
*/
public function run()
{
\App\Models\Student::factory(100)->create();
}
}
Concept
\App\Models\Student::factory(100)->create();It will generate 100 fake rows of student using StudentFactory.php file and save into students table.
Run Data Seeder
Back to project terminal and run this command to run factory to seed fake data.
$ php artisan db:seedIt will generate and save fake data into students table.
Install Yajra Datatable
To install yajrabox, we need to run a composer command. Open up the project terminal and type this command and execute.
$ composer require yajra/laravel-datatables-oracleWhile installation of this package, you will get such type of screen over terminal.
Create Controller
Open project into terminal and run this command into it.
$ php artisan make:controller StudentControllerIt will create StudentController.php file inside /app/Http/Controllers folder. Open controller file and write this code into it.
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Models\Student;
use Yajra\DataTables\DataTables;
class StudentController extends Controller
{
public function index(Request $request)
{
if ($request->ajax()) {
$data = Student::select('*');
return Datatables::of($data)
->addIndexColumn()
->addColumn('gender', function ($row) {
return ucfirst($row['gender']);
})
->addColumn('action', function ($row) {
$btn = '<a href="javascript:void(0)" data-id="' . $row['id'] . '" class="edit btn btn-success btn-sm text-center">View</a>';
return $btn;
})
->rawColumns(['action'])
->make(true);
}
return view('student');
}
}
Concept
$data = Student::select('*');
return Datatables::of($data)
->addIndexColumn()
->addColumn('gender', function ($row) {
return ucfirst($row['gender']);
})
->addColumn('action', function ($row) {
$btn = '<a href="javascript:void(0)" data-id="' . $row['id'] . '" class="edit btn btn-success btn-sm text-center">View</a>';
return $btn;
})
->rawColumns(['action'])
->make(true);Create Template
Create a fie student.blade.php inside /resources/views folder. Open student.blade.php and write this content into it.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>How to Use Yajra Datatables in Laravel 9</title>
<meta name="csrf-token" content="{{ csrf_token() }}">
<link href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/twitter-bootstrap/5.0.1/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<link href="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.11.4/css/dataTables.bootstrap5.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h3 class="text-center mt-3 mb-4">How to Use Yajra Datatables in Laravel 9</h3>
<table class="table table-bordered data-table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>No</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>Mobile</th>
<th>Gender</th>
<th width="100px" class="text-center">Action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.1.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.11.4/js/jquery.dataTables.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.datatables.net/1.11.4/js/dataTables.bootstrap5.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
$(function() {
var table = $('.data-table').DataTable({
processing: true,
serverSide: true,
ajax: "{{ route('students.index') }}",
columns: [{
data: 'id',
name: 'id'
},
{
data: 'name',
name: 'name'
},
{
data: 'email',
name: 'email'
},
{
data: 'mobile',
name: 'mobile'
},
{
data: 'gender',
name: 'gender'
},
{
data: 'action',
name: 'action',
orderable: false,
searchable: false
},
]
});
});
</script>
</html>
Add Route
Open web.php file from /routes folder. Add this route into it.
//...
use App\Http\Controllers\StudentController;
//...
Route::get('students', [StudentController::class, 'index'])->name('students.index');
Application Testing
Run this command into project terminal to start development server,
php artisan serveURL – http://127.0.0.1:8000/students
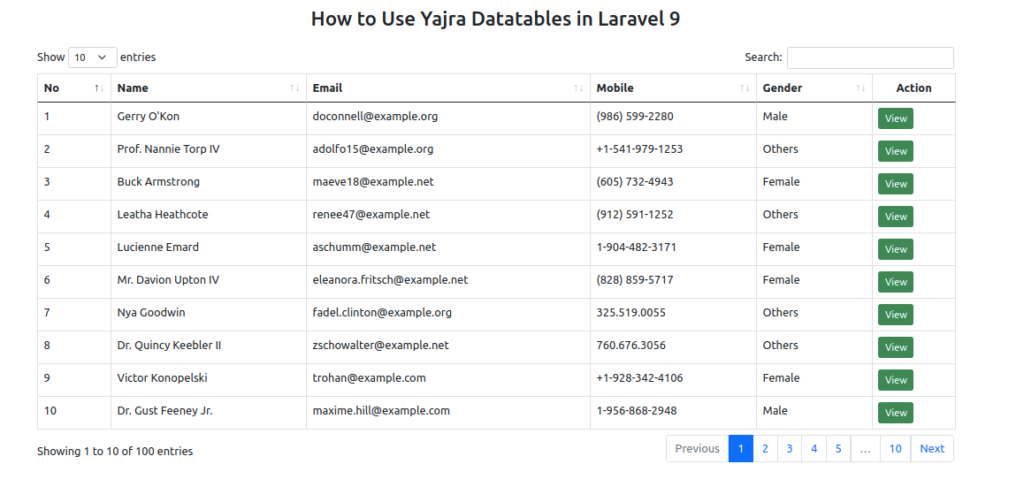
We hope this article helped you to learn about Laravel 9 YajraBox Server Side Datatable Tutorial in a very detailed way.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for PHP & it’s framework, WordPress, Node Js video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
Read more