Seeding a Laravel database with JSON data is an important step in web development since it allows you to populate your database with organised, predetermined data. Laravel, a versatile and resilient PHP framework, provides quick methods for seeding your database with JSON data, a popular and adaptable data storage format.
Database seeding is the process in which we feed test data to tables. We can insert data either using Faker library, manual data or means of some more data sources like CSV, JSON.
In this video, we will walk you through the process of seeding JSON data in Laravel 10, giving you the knowledge and tools you need to properly manage your database.
Read More: Laravel 10 Google Line Chart Integration Example Tutorial

Let’s get started.
Laravel Installation
Open terminal and run this command to create a laravel project.
composer create-project laravel/laravel myblogIt will create a project folder with name myblog inside your local system.
To start the development server of laravel –
php artisan serveURL: http://127.0.0.1:8000
Assuming laravel already installed inside your system.
Create Database & Connect
To create a database, either we can create via Manual tool of PhpMyadmin or by means of a mysql command.
CREATE DATABASE laravel_app;
To connect database with application, Open .env file from application root. Search for DB_ and update your details.
DB_CONNECTION=mysql DB_HOST=127.0.0.1 DB_PORT=3306 DB_DATABASE=laravel_app DB_USERNAME=root DB_PASSWORD=root
Create Model and Migration
Open project terminal and run this command to create model and migration file,
php artisan make:model Country -mIt will create two files –
- Model – Country.php inside /app/Models folder
- Migration file – xxx_create_countries_table inside /database/migrations folder.
Read More: How To Seed CSV Data in Laravel 10 Example Tutorial
Open file and write this complete code into it,
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function up(): void
{
Schema::create('countries', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('sortname');
$table->string('name');
$table->string('phonecode');
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*
* @return void
*/
public function down(): void
{
Schema::dropIfExists('countries');
}
};
Open model file Country.php and write this complete code into it.
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Factories\HasFactory;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Country extends Model
{
use HasFactory;
public $timestamps = false;
}
Run Migration
Next, we need to migrate migration files.
php artisan migrateThis command will create tables inside database. It will create countries table in database.
Prepare JSON Data File (A Set of Data)
As you have table countries in which columns as id, name, sortname, phonecode.
You have a JSON file in which properties of each object will be ID, Sortname, Name & Phonecode. Rest we need data into it.
When you will download the given file it will be in .txt format.
Rename file into .json and place this countries-data.json file inside /public/data folder.
Read More: Laravel 10 Mailable Email Template Components Tutorial
Open countries-data.json file, you should see –

Create Laravel Data Seeder
Next, you need to create a seeder file.
php artisan make:seeder CountrySeederIt will create a file CountrySeeder.php inside /database/seeders folder.
Open file and write this complete code into it.
<?php
namespace Database\Seeders;
use Illuminate\Database\Console\Seeds\WithoutModelEvents;
use Illuminate\Database\Seeder;
use App\Models\Country;
use File;
class CountrySeeder extends Seeder
{
/**
* Run the database seeds.
*/
public function run()
{
//Country::truncate();
$json = File::get(public_path("data/countries-data.json"));
$countries = json_decode($json);
foreach ($countries->countries as $key => $value) {
Country::create([
"sortname" => $value->sortname,
"name" => $value->name,
"phonecode" => $value->phoneCode
]);
}
}
}
Laravel Data Seeding
Open project terminal and run this artisan command
php artisan db:seed --class=CountrySeederIt will seed countries data into table.
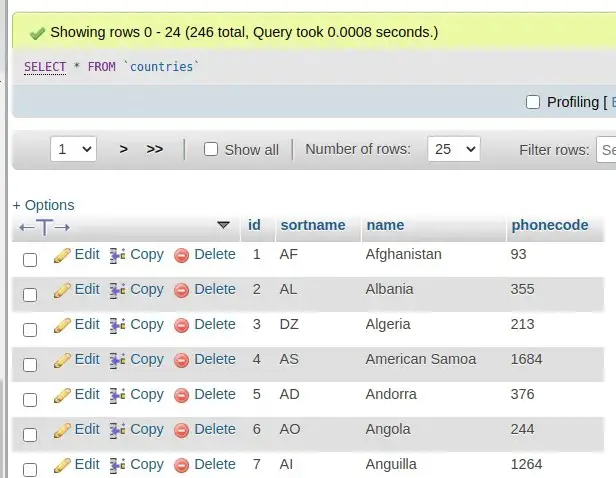
Successfully, you can see we have imported JSON data into database table using Laravel Data Seeding Concept.
That’s it.
We hope this article helped you to learn about How To Seed JSON Data in Laravel 10 Example Tutorial in a very detailed way.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for PHP & it’s framework, WordPress, Node Js video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
Read more