When we work with MySQL Queries, then definitely for some relational data we need to work with Joins. Inside this article we will see the concept of Inner Join in CodeIgniter 4.
Joins in CodeIgniter 4 is the connection between one and more tables to get data. In MySQL we have Inner join, Left join, Right join, Outer join.
We will see the concept of Inner Join in this CodeIgniter 4 article.
Learn More –
- Working with MySQL Joins in CodeIgniter 4.
- CodeIgniter 4 Redirection Complete Tutorial
- Codeigniter 4 Remove Public and Index.php From URL
- CodeIgniter 4 RESTful APIs with JWT Authentication
Let’s get started.
Types of Joins available in CodeIgniter 4
In CodeIgniter 4 application, as per the documentation we have 3 types of joins available. Here are the followings –
- Inner Join
- Left Join
- Right Join
What is Inner Join?
Inner Join – This join brings the data on the basis of a common value condition between two or more than two tables. According to matched condition it will bring all data what we expected for. It remove those rows from result set which has no matched condition.
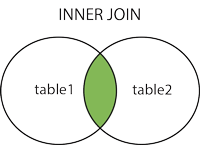
How can we use inside an application and get relational data we will see by making an application. Let’s create an application in which we use Inner Join.
CodeIgniter 4 Installation
To create a CodeIgniter 4 setup run this given command into your shell or terminal. Please make sure composer should be installed.
composer create-project codeigniter4/appstarter codeigniter-4Assuming you have successfully installed application into your local system.
Environment (.env) Setup
When we install CodeIgniter 4, we will have env file at root. To use the environment variables means using variables at global scope we need to do env to .env
Either we can do via renaming file as simple as that. Also we can do by terminal command.
Open project in terminal
cp env .envAbove command will create a copy of env file to .env file. Now we are ready to use environment variables.
Enable Development Mode
CodeIgniter starts up in production mode by default. You need to make it in development mode to see any error if you are working with application.
Open .env file from root.
# CI_ENVIRONMENT = production
// Do it to
CI_ENVIRONMENT = developmentNow application is in development mode.
Create Database
To create a database, either we can create via Manual tool of PhpMyadmin or by means of a mysql command.
We will use MySQL command to create database. Run this command into Sql tab of PhpMyAdmin.
CREATE DATABASE codeigniter4_app;Successfully, we have created a database.
Create Database Table
Next, we need tables. That table will be responsible to store data.
Let’s create two tables with some columns.
CREATE TABLE `tbl_users` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(120) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(120) DEFAULT NULL,
`phone_no` varchar(120) DEFAULT NULL,
`created_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
CREATE TABLE `tbl_courses` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(120) NOT NULL,
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1Table tbl_courses contains user_id column on the basis of which we are going to make use of join. Successfully, we have created two tables.
Let’s insert some dummy data into these tables.
Database Connection
Open .env file from project root.
Search for DATABASE. You should see the connection environment variables into it. Put your updated details of database connection string values.
#-------------------------------------------------------------------- # DATABASE #-------------------------------------------------------------------- database.default.hostname = localhost database.default.database = codeigniter4_app database.default.username = admin database.default.password = admin database.default.DBDriver = MySQLi database.default.DBPrefix = database.default.port = 3306
Now, database successfully connected with the application.
Creating Test data for Application
Here we have some sql queries, you need to copy and run into database. It will inserts data into tables.
Test data for tbl_users –
-- -- Dumping data for table `tbl_users` -- INSERT INTO `tbl_users` (`id`, `name`, `email`, `phone_no`, `created_at`) VALUES (1, 'Sanjay', 'sanjay@gmail.com', '8527419630', '2020-09-10 13:19:38'), (2, 'Vijay', 'vijay@gmail.com', '9875643125', '2020-09-25 11:33:00'), (3, 'Ashish Kumar', 'ashish@gmail.com', '7896541230', '2020-09-25 11:33:17');
Test data for tbl_courses –
-- -- Dumping data for table `tbl_courses` -- INSERT INTO `tbl_courses` (`id`, `name`, `user_id`) VALUES (1, 'Learn CodeIgniter 4', 1), (2, 'Learn PHP', 2), (3, 'Learn CakePHP 4', 30), (4, 'Learn Laravel', 35);
To Learn about Seeders in CodeIgniter 4, Click here.
Create Routes
Open Routes.php from /app/Config. Add this route into this file.
//..
$routes->get('inner-join', 'Site::innerJoinMethod');
Create Controller
Next,
Open project into terminal and run this spark command to create controller.
$ php spark make:controller SiteIt will create Site.php at /app/Controllers folder.
Open Site.php and write this complete code into it.
<?php
namespace App\Controllers;
use App\Controllers\BaseController;
class Site extends BaseController
{
private $db;
public function __construct()
{
$this->db = db_connect(); // Loading database
// OR $this->db = \Config\Database::connect();
}
public function innerJoinMethod()
{
$builder = $this->db->table("tbl_users as user");
$builder->select('user.*, course.name as course_name');
$builder->join('tbl_courses as course', 'user.id = course.user_id');
$data = $builder->get()->getResult();
echo "<pre>";
print_r($data);
// To print query
// $this->db->getLastQuery();
}
//...
}Behind the scene executed query is –
SELECT `user`.*, `course`.`name` as `course_name` FROM `tbl_users` as `user` JOIN `tbl_courses` as `course` ON `user`.`id` = `course`.`user_id`Application Testing
Open project terminal and start development server via command:
php spark serveURL – http://localhost:8080/inner-join
Have a look output –
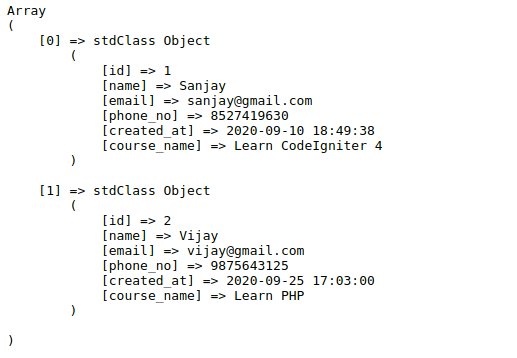
We are getting only matched rows according to the condition user.id = course.user_id
We hope this article helped you to learn MySQL Inner join in codeigniter 4 in a very detailed way.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for PHP & it’s framework, WordPress, Node Js video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
Read more