Inside this article we will see the concept i.e CodeIgniter 4 How To Submit Form Data by Ajax Request. Article contains the classified information about How to use Ajax requests in application to save form data to database.
CodeIgniter 4 is a open source PHP Framework. Nowadays, every application somewhere uses Ajax request either for any operations like Create, Read, Update & Delete in CodeIgniter 4.
Inside this tutorial we will create a form with few input fields and upload in codeIgniter 4 using Ajax request. This CodeIgniter 4 form data submit by ajax is a very interesting topic to implement. This article will help you to understand in a very easy way.
Learn More –
- CodeIgniter 4 Upload Image using Ajax Method
- Image Upload with Preview Using Ajax in CodeIgniter 4
- How To Create CodeIgniter 4 CRUD REST APIs Development
- CodeIgniter 4 How To Work with Form Validation Library
Let’s get started.
CodeIgniter 4 Installation
To create a CodeIgniter 4 setup run this given command into your shell or terminal. Please make sure composer should be installed.
composer create-project codeigniter4/appstarter codeigniter-4Assuming you have successfully installed application into your local system.
Now, let’s configure database and application connectivity.
Environment (.env) Setup
When we install CodeIgniter 4, we will have env file at root. To use the environment variables means using variables at global scope we need to do env to .env
Either we can do via renaming file as simple as that. Also we can do by terminal command.
Open project in terminal
cp env .envAbove command will create a copy of env file to .env file. Now we are ready to use environment variables.
Enable Development Mode
CodeIgniter starts up in production mode by default. You need to make it in development mode to see any error if you are working with application.
Open .env file from root.
# CI_ENVIRONMENT = production
// Do it to
CI_ENVIRONMENT = developmentNow application is in development mode.
Create Database
To create a database, either we can create via Manual tool of PhpMyadmin or by means of a mysql command.
We will use MySQL command to create database. Run this command into Sql tab of PhpMyAdmin.
CREATE DATABASE codeigniter4_app;Successfully, we have created a database.
Create Database Table
Next, we need a table. That table will be responsible to store data.
Let’s create table with some columns.
CREATE TABLE `users` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(120) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(120) DEFAULT NULL,
`mobile` varchar(45) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;Successfully, we have created a table. Let’s connect with the application.
Database Connection
Open .env file from project root.
Search for DATABASE. You should see the connection environment variables into it. Put your updated details of database connection string values.
#-------------------------------------------------------------------- # DATABASE #-------------------------------------------------------------------- database.default.hostname = localhost database.default.database = codeigniter4_app database.default.username = admin database.default.password = admin database.default.DBDriver = MySQLi database.default.DBPrefix = database.default.port = 3306
Now, database successfully connected with the application.
Add Routes
Open Routes.php from /app/Config folder. Add these routes into it.
//...
$routes->get("add-user", "UserController::addUser");
$routes->post("save-user", "UserController::saveUser");
//...
Let’s create Model.
Create Model
Open project into terminal and run this spark command to create model.
$ php spark make:model User --suffixIt will create UserModel.php inside /app/Models folder. Open that file and write this complete code into it.
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use CodeIgniter\Model;
class UserModel extends Model
{
protected $DBGroup = 'default';
protected $table = 'users';
protected $primaryKey = 'id';
protected $useAutoIncrement = true;
protected $insertID = 0;
protected $returnType = 'array';
protected $useSoftDelete = false;
protected $protectFields = true;
protected $allowedFields = [
"name",
"email",
"mobile"
];
// Dates
protected $useTimestamps = false;
protected $dateFormat = 'datetime';
protected $createdField = 'created_at';
protected $updatedField = 'updated_at';
protected $deletedField = 'deleted_at';
// Validation
protected $validationRules = [];
protected $validationMessages = [];
protected $skipValidation = false;
protected $cleanValidationRules = true;
// Callbacks
protected $allowCallbacks = true;
protected $beforeInsert = [];
protected $afterInsert = [];
protected $beforeUpdate = [];
protected $afterUpdate = [];
protected $beforeFind = [];
protected $afterFind = [];
protected $beforeDelete = [];
protected $afterDelete = [];
}Create Controller
Open project into terminal and run this spark command to create controller.
$ php spark make:controller User --suffixThis command will create a file UserController.php inside /app/Controllers folder.
Open UserController.php and write this complete code into it.
<?php
namespace App\Controllers;
use App\Models\UserModel;
class UserController extends BaseController
{
public function __construct()
{
helper(["url"]);
}
public function addUser()
{
// layout of add user form
return view('add-user');
}
public function saveUser()
{
if ($this->request->getMethod() == "post") {
$rules = [
"name" => "required",
"email" => "required|valid_email",
"mobile" => "required"
];
if (!$this->validate($rules)) {
$response = [
'success' => false,
'msg' => "There are some validation errors",
];
return $this->response->setJSON($response);
} else {
$userModel = new UserModel();
$data = [
"name" => $this->request->getVar("name"),
"email" => $this->request->getVar("email"),
"mobile" => $this->request->getVar("mobile"),
];
if ($userModel->insert($data)) {
$response = [
'success' => true,
'msg' => "User created",
];
} else {
$response = [
'success' => true,
'msg' => "Failed to create user",
];
}
return $this->response->setJSON($response);
}
}
}
}Create Layout File
Create add-user.php inside /app/Views folder.
Open add-user.php and write this complete code into it.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>CodeIgniter 4 Form Data Submit by Ajax Method</title>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.4.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/sweetalert2@9.17.2/dist/sweetalert2.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<style>
#frm-add-user label.error{
color:red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h4 style="text-align: center;">CodeIgniter 4 Form Data Submit by Ajax Method</h4>
<div class="panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading">CodeIgniter 4 Form Data Submit by Ajax Method</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<form class="form-horizontal" action="javascript:void(0)" id="frm-add-user">
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label col-sm-2" for="name">Name:</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="text" class="form-control" required id="name" placeholder="Enter name" name="name">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label col-sm-2" for="email">Email:</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="email" class="form-control" required id="email" placeholder="Enter email" name="email">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label class="control-label col-sm-2" for="mobile">Mobile:</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="text" class="form-control" required id="mobile" placeholder="Enter mobile" name="mobile">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-sm-offset-2 col-sm-10">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.5.1/jquery.min.js"></script>
<!-- Validation library file -->
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery-validate/1.19.2/jquery.validate.min.js"></script>
<!-- Sweetalert library file -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/sweetalert2@9.17.2/dist/sweetalert2.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function() {
// Adding form validation
$('#frm-add-user').validate();
// Ajax form submission with image
$('#frm-add-user').on('submit', function(e) {
e.preventDefault();
var formData = new FormData(this);
// OR var formData = $(this).serialize();
//We can add more values to form data
//formData.append("key", "value");
$.ajax({
url: "<?= site_url('save-user') ?>",
type: "POST",
cache: false,
data: formData,
processData: false,
contentType: false,
dataType: "JSON",
success: function(data) {
if (data.success == true) {
Swal.fire('Saved!', '', 'success')
}
},
error: function(jqXHR, textStatus, errorThrown) {
alert('Error at add data');
}
});
});
});
</script>- $(“#frm-add-user”).validate(); Using validate method validation library. As you can see inside view file code we have also added jquery.validate.min.js This is for client side form validation.
- var formData = new FormData(this); Process all form data
- var formData = $(this).serialize(); Store form data in serialized format.
- $.ajax({}); Using ajax method of jQuery. This method have some properties as you can see we have used in the ajax request configuration.
Application Testing
Open project terminal and start development server via command:
php spark serveURL – http://localhost:8080/add-user
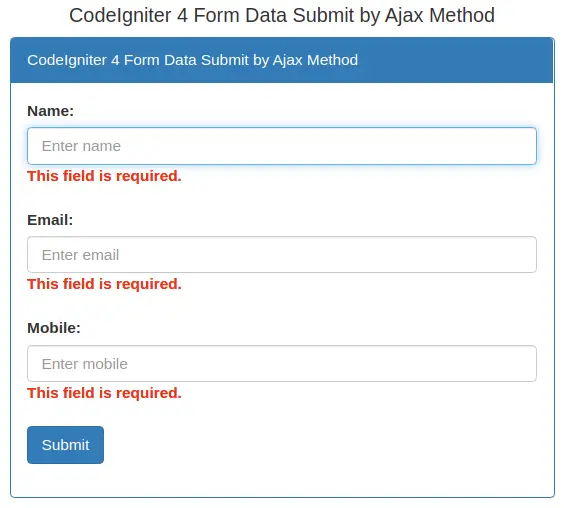
Submit form without any data
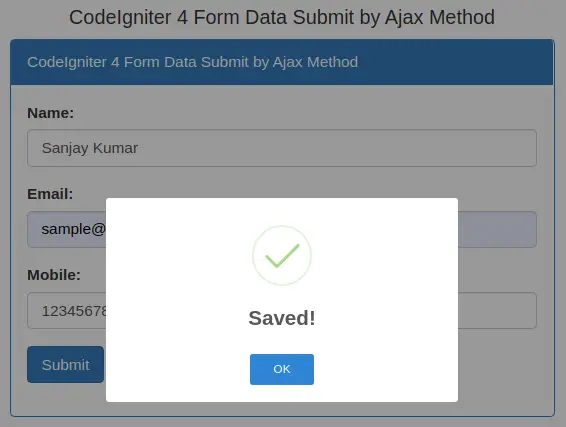
Let’s fill some data and press submit button to initiate Ajax request and to save data into table.
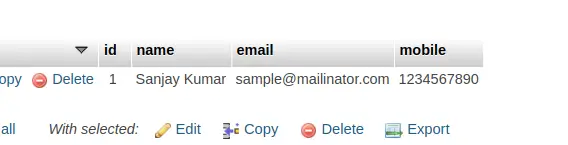
Data saved in database table
We hope this article helped you to learn about CodeIgniter 4 How To Submit Form Data by Ajax Request in a very detailed way.
Online Web Tutor invites you to try Skillshike! Learn CakePHP, Laravel, CodeIgniter, Node Js, MySQL, Authentication, RESTful Web Services, etc into a depth level. Master the Coding Skills to Become an Expert in PHP Web Development. So, Search your favourite course and enroll now.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for PHP & it’s framework, WordPress, Node Js video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
Sir g thanks a lot whenever i need something i found on your site only and the way of explaining is just amazing
Thanks
hello sir,i just want to request that please ad check email availability in your ajax form.i mean when user submit the button it should be check whether the given email is exist or not.if yes then it should be redirect to signup form.please it’s my humble request.
Hi sir nice Ci4 tutorials how , suggests me a tutorial to make a news websites
ThanThanksks